Chemistry Concepts: Solutions, Reactions, and Elements
What is mole fraction?
Mole fraction represents the number of molecules of a particular component in a mixture divided by the total number of moles in the given mixture. It’s a way of expressing the concentration of a solution.
Define formality and provide its formula.
“Formality is defined as the number of gram formula mass of solute dissolved per liter of solution.” It is used for ionic compounds. The formality of the solution is denoted by the symbol F. It is similar to normality.
What is the difference between an ideal and a non-ideal solution?
| Ideal Solution | Non-Ideal Solution |
|---|---|
| They follow Raoult’s rules. | They don’t follow Raoult’s rules. |
| The solute-solvent molecular interactions are identical to that of pure components. | The interaction between solute & the solvent is lower or higher than the connection among pure components. |
| Raoult’s law predicts that the overall vapor pressure will be the same. | According to Raoult’s law, the absolute vapor pressure increases or lowers the projected value. |
| The enthalpy of mixing, Hmix = 0, is zero since no heat is emitted or absorbed. | Heat will be either emitted or absorbed, resulting in a positive or negative enthalpy of mixing, Hmix ≠ 0. |
| Because the overall volume equals the sum of the component volumes (solute & solvent), the volume of the mixture is zero, Vmix = 0. | Vmix is not zero since the volume of blending is not zero. Either volume change occurs. |
| Fractional distillation can be used to separate components. | Fractional distillation cannot separate components in their pure form. |
| Hexane & heptane, for example, are benzene & toluene derivatives. All of the dilute behave almost exactly like an ideal solution. | Carbon disulfide & acetone, phenol & aniline, chloroform & acetone, & so on. |
What is the difference between molarity and molality?
| Molarity | Molality |
|---|---|
| As mentioned, it relates to the volume of the solution, so we can say the total number of moles per liter of solution is termed as molarity. | As we know it is related to the mass, so it is defined as the total moles of a solute present in a kilogram of a solvent is termed to be molality. |
| From the definition; it depends on the volume of the solution. | It is dependable on the mass of the solution, from the definition. |
| The unit of molarity is expressed as M. | The unit of molality is expressed as m. |
| Molarity can be determined by dividing moles of the solute to that of the volume of solution in liters. | Molality can be determined by dividing the moles of solute to that of the mass of solvent in kilograms. |
| The unit of molarity can be derived i.e. moles/liter. | The unit of molality can be derived i.e. moles/kg. |
The IUPAC name of [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 is hexaamminecobalt(III) chloride.
The IUPAC name for K2[PdCl4] is potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II).
The formula for the coordination compound pentacarbonyliron(0) is Fe(CO)5.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA is double-stranded, forming a double helix, while RNA is usually single-stranded. The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, whereas RNA contains ribose. Furthermore, DNA uses the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, while RNA uses adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine.
Define zwitterion and give an example.
A zwitterion is a functional group molecule in which at least one has a positive electrical charge and one a negative electrical charge. The whole molecule’s net charge is zero. The best-known examples of zwitterions are amino acids. They have an amine group (basic) and a carboxyl group (acidic).
Reaction of ethyl chloride in aq. KOH:
It gives ethyl alcohol and HCl as the products. In the reaction, chloride is a good leaving group, and hydroxide will attack at the alpha carbon from the back, making and breaking will happen at the same time.
When methyl chloride reacts with potassium cyanide (KCN), it undergoes a substitution reaction to produce methyl cyanide.
Faraday’s Law of Electrolysis:
Faraday’s First Law of Electrolysis
It is one of the primary laws of electrolysis. It states that during electrolysis, the amount of chemical reaction which occurs at any electrode under the influence of electrical energy is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte.
Faraday’s Second Law of Electrolysis
Faraday’s second law of electrolysis states that if the same amount of electricity is passed through different electrolytes, the masses of ions deposited at the electrodes are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents.
From these laws of electrolysis, we can deduce that the amount of electricity needed for oxidation-reduction depends on the stoichiometry of the electrode reaction.
Conversion of formaldehyde to acetaldehyde:

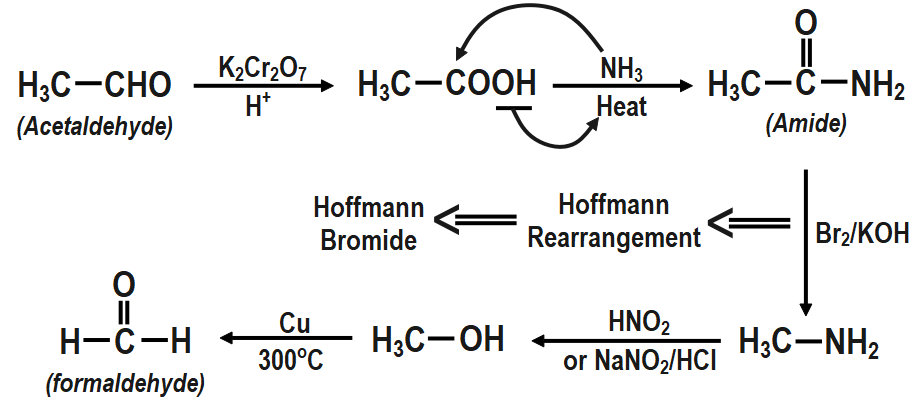
Conversion of acetaldehyde to formaldehyde:
Mechanism of SN1 and SN2 reaction:
Mechanism of SN2 reaction:
Formation of carbocation Attack of nucleophile
What is the difference between d-block and f-block elements?
d-Block elements: d-Block contains elements from group 3 to group 12. It is present in the middle of the modern periodic table. They are also known as transition elements. The last electron in the d-block elements enters in d orbital. General outer electronic configuration of d-block elements is ns0-2 (n-1)d1-10. e.g. Cu, Zn, Cr, Ti, V, etc.
f-Block elements: f-Block contains elements of lanthanide and actinide series. f-block elements are present below the modern periodic table as two separate rows. They are also known as inner transition elements. The last electron in the f-block elements enters in f orbital. General outer electronic configuration of f-block elements is ns2 (n-1) d0-1 (n – 2) f1-14. e.g. Ce, Pr, Nd Th, U, Np, etc
