Environmental Science: Systems, Cycles, and Human Impact
Interconnectedness & Systems Thinking
- Interconnectedness: All components of the environment are linked; changes affect the entire system.
- Systems: Closed/Open; feedback loops:
- Negative Feedback: Stabilizes (e.g., predator-prey dynamics)
- Positive Feedback: Amplifies changes (e.g., melting ice reduces albedo).
- Dynamic Equilibrium: Interactions between atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere.
- Fossil Record: Evolutionary history of life on Earth.
Geological Cycles
- Rock Cycle: Igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic rocks; driven by melting, cooling, erosion.
- Tectonic Cycle: Plate movements; earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain-building.
- Plate Boundaries:
- Divergent: Plates move apart.
- Convergent: Plates move together (subduction, continental collision).
- Transform: Plates slide past each other.
Biodiversity & Ecosystems
- Ecosystem Services: Provisioning (food, water), regulating (climate), supporting (nutrient cycling), cultural (recreation).
- Primary Productivity: Energy from photosynthesis supports ecosystems.
- Trophic Levels: Energy decreases at each level; Keystone Species: Critical for ecosystem structure.
Biodiversity Loss: Driven by habitat destruction, climate change, invasive species, pollution.
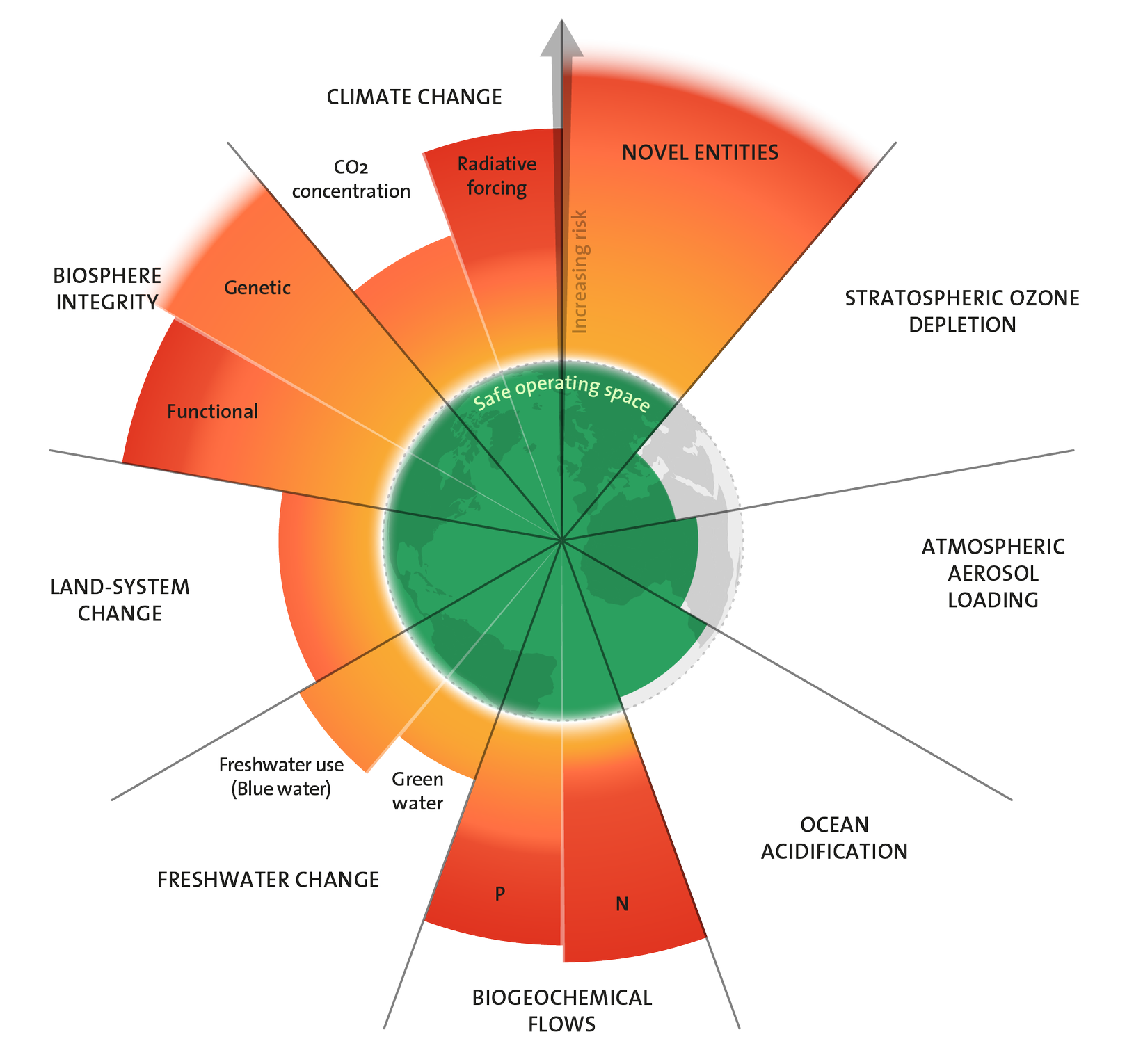
Human Impact
- Degradation: Erosion, desertification due to agriculture, deforestation.
- Anthropocene: Human-dominated geological epoch.
- Sustainable Practices: Crop rotation, agroforestry, conservation tillage.
Environmental Health & Pollution
- Air Pollution: Sources include industry, transportation; Indoor Pollutants: Radon, VOCs, mold.
- Acid Rain: Sulfur/nitrogen oxides + water = acid deposition; harmful to ecosystems.
Energy Resources
- Fossil Fuels: Coal, oil, gas; high environmental impact (GHG emissions, pollution).
- Renewable Energy: Solar, wind, hydropower; clean, sustainable alternatives.
- Nuclear Energy: Low emissions; challenges with waste and safety.
- Sustainability: Efficient resource use, reducing waste, renewable technologies.
Water Resources & Oceanography
- Hydrologic Cycle: Water movement (evaporation, condensation, precipitation).
- Ocean Structure: Stratified by temperature, salinity; currents affect climate.
- Marine Ecosystems: Coral reefs, estuaries; threatened by pollution, overfishing.
Environmental Policy & Ethics
- Policy Tools: Regulations, incentives, market-based approaches.
- Ethics: Anthropocentrism (human-centered), biocentrism (life-centered), ecocentrism (ecosystem-centered).
- Indigenous Knowledge: Incorporating TEK into environmental management.
