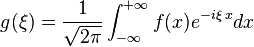Mathematics Cheat Sheet: Derivatives, Vectors, Probability, and More
Derivative Table
f (x) = K f ‘(x) = 0
f (x) = x f ‘(x) = 1
f (x) = kx f ‘(x) = k
f (x) = kx + b f ‘(x) = k
f (x) = xn f ‘(x) = nxn-1
f (x) = u (x) + v (x) f ‘(x) = u’ (x) + v ‘(x)
f (x) = u (x) * v (x) f ‘(x) = u (x) * v’ (x) + v (x) * v ‘(x)
f (x) = u (x) / v (x) f ‘(x) = [v (x) * u’ (x) – u (x) * v ‘(x)] / [v (x)]2
f (x) = [u (x)]n f ‘(x) = n[u (x)]n-1 * u’ (x)
f (x) = sin x f ‘(x) = cos x
f (x) = sin [u (x)] f ‘(x) = cos u * u’
f (x) = cos x f ‘(x) = – sin x
f (x) = cos u f ‘(x) = – sin u * u’
f (x) = tan x f ‘(x) = sec2 x
f (x) = tan u f ‘(x) = sec2 u * u’
f (x) = cot x f ‘(x) = -csc2 x
f (x) = cot u f ‘(x) = -csc2 u * u’
f (x) = sec x f ‘(x) = sec x * tan x
f (x) = sec u f ‘(x) = tan u sec u * u’
f (x) = csc x f ‘(x) = – csc x * cot x
… (Continued)
Posted by ANTHRAX and classified in Mathematics Chops of Secondary .
Posted November 28, 2007 in  Spanish and with a size of 9938 bytes.
Spanish and with a size of 9938 bytes.

Vector Sum
Graphically, you can add vectors by two methods: the parallelogram and the polygon. The parallelogram method basically consists of reproducing the two vectors in contrast. That is, if there is a vector called “a” and another called “b”, in the parallelogram method, the reproduction of “b” would be at the end of “a” and vice versa, forming a parallelogram. The result would be obtained by joining the central point to where the reproductions of “a” and “b” meet. The triangle method is similar to the polygon method. The difference is that the triangle method only admits two vectors, and in the polygon method, two of the triangle method are made one after the other. That is, we have vector “a” and vector “b”; vector “b” starts where vector “a” ends. To obtain the resultant, you only join the starting point to where it ends.
Posted by Chops Program and classified in Mathematics Chops of Training.
Written on June 22, 2007 in  Spanish and with a size of 4179 bytes.
Spanish and with a size of 4179 bytes.

Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
Descriptive statistics: Classification and description of a dataset.
Inferential statistics: Interpreting the results obtained with the descriptive techniques for making decisions.
Statistician: Global descriptive feature of a total sample of research.
Frequency polygon: Graphic lines usually plotted on a frequency histogram.
… (Continued)Submitted by Anonymous and classified in Mathematics Chops of University .
Written on January 17, 2008 in  Spanish and with a size of 9365 bytes.
Spanish and with a size of 9365 bytes.
Algorithm
Algorithm (Perhaps from Lat. algobarismus, late *, and this Abbrev. AR. Class.? is? bu l? ub? r, calculation using Arabic numerals). 1. A finite ordered set of operations that allows the solution to a problem. 2. Method and notation in different ways to calculate.
Posted by ANTHRAX and classified in Mathematics Chops of Bachiller .
Posted on 04 December 2007 in  Spanish and with a size of 1601 bytes.
Spanish and with a size of 1601 bytes.
In mathematics, especially in linear algebra, a matrix of dimensions n × n is said to be invertible, nonsingular, or regular if there is a matrix B of dimensions n × n such that AB = BA = In,
where In denotes the identity matrix of order n (dimension n × n) and the product used is the usual matrix product. A matrix that is not invertible is said to be a singular matrix.
The inverse of the matrix A is unique. This is denoted by A-1.
Properties of the Inverse Matrix
The inverse of the product of two matrices is the product of changing the reverse order:
… (Continued)Posted by Chops Program and classified in Mathematics Chops of Secondary .
Posted on 04 March 2008 in  Spanish and with a size of 2360 bytes.
Spanish and with a size of 2360 bytes.
Company Departments
Departments:
– Production Department: This is the one who is responsible for developing the product with which the company sells. In the Company of the tertiary sector do not exist.
– Finance Department: Responsible for seeking alternative sources of funding for the company.
– Human Resources Department: Its main function is to select and recruit workers, formalize contracts, process payroll and social insurance, in addition to ensuring compliance with labor laws. They are in charge of relations with the entire team of the company.
– Business Department: The marketing function includes all activities necessary to reach the consumer goods and services produced by the company. Through these functions, 3 subfunctions are performed that are … (Continued)
Posted by Chops Program and classified in Mathematics Chops of Secondary .
Posted December 13, 2006 in  Spanish and with a size of 6126 bytes.
Spanish and with a size of 6126 bytes.
Bodies and Substance
Bodies and substance: Physics, biological and geological.
Subject: What extends all the way and can boast.
Kinds of matter: Melting point, density, smell, taste, color …
General properties: Mass, volume …
Body:
External properties: Shape, volume, area, length …
Internal properties: They depend on the nature of the substance that is formed.
Materials systems: Well-defined set of material bodies. Each one of these bodies is known as a component of the system.
Open: If matter and energy exchange with the outside.
Closed: If the foreign exchange only energy, no matter.
Isolated: If it is impossible any exchange of matter and energy with the outside.
… (Continued)
Submitted by Anonymous and classified in Mathematical Notes of the University .
Written on January 28, 2008 in  Spanish and with a size of 13,898 bytes.
Spanish and with a size of 13,898 bytes.
Fourier Transform
In mathematics, the Fourier transform is an application that maps to a function f with real or complex values and defined in the line, another function g defined as follows:
|
Where f is L1, or f has to be an integrable function in the sense of the Lebesgue integral.
Sort by …
Type
Subjects
- Other materials
- Language Arts
- History
- Philosophy
Mathematics
- Biology
- Physics
- Chemistry
- English
- Geography
- Computing
- Electronics
- Economy
- Social Sciences
- Right
- Teaching and Education
- Health Sciences
- Training and Employment Guidance (FOL)
- Value in the Work Environment (RET)
- French
- Spanish
- Technology
- Geology
- Music
- Religion
- Physical Education