Natural and Man-Made Landscapes: Types and Impacts
Landscapes
A Landscape is Everything We Can See in an Area.

There Are Different Types of Landscape:
- Natural Landscapes: Natural features. They form very slowly over millions of years.

- Man-made Landscapes: Humans have changed the environment.

Types of Natural Landscapes: Inland (Away from the Sea) and Coastal (Near the Sea)
Landforms in Natural Inland Landscapes

- Mountains: Large inclines of rocky land that rise from the ground.

Parts of a Mountain: Summit, Foot, and Slope
- Summit: Top of a mountain.
- Foot: Bottom of a mountain.
- Slope: Part between the summit and the foot of a mountain.

A group of mountains is a mountain range.

- Hills: Small, rounded elevations of land on plains. Hills are lower than mountains.


- Plateaus: Flat areas of land higher than plains (+600m above sea level).


- Valleys: Areas of land between mountains. There are usually rivers in valleys.

- Depression: Land that sinks below the surrounding area.
- Plains: Wide, flat areas.

Landforms in Natural Coastal Landscapes

- Bay: Where the sea extends into the land.

- A large bay is a gulf.

- Beach: Low, flat area of sand or rocks next to the sea.

- Headland or Cape: Land that extends into the sea.


- Cliff: A very high, steep wall of rock next to the sea.
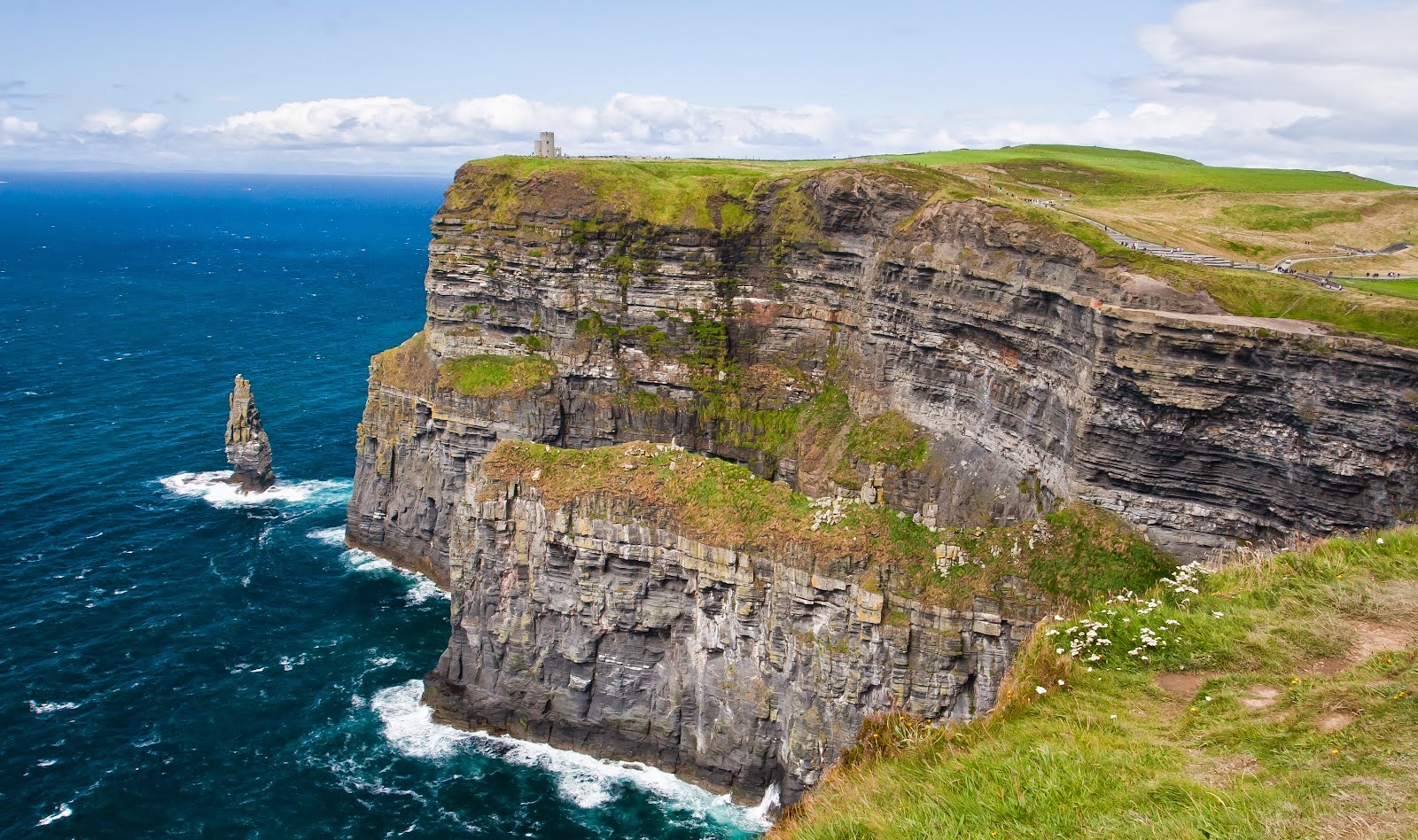

- Island: Land surrounded by water.

- Archipelago: Group of islands.

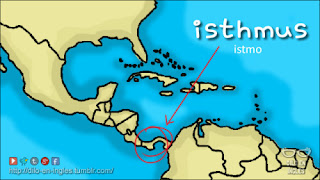
- Peninsula: Land surrounded by water on three sides.



- Isthmus: Strip of land that connects the peninsula to the mainland.
Man-Made Changes: Made by Humans
Man-made Features:
Infrastructures for Transport: Enable communication, help industry and economy, encourage tourism.
- Roads

- Motorways

- Railways

- Airports and Ports


- Docks

Man-made Structures to Form Economic Activity: Create employment and need for services (shops, hospitals, etc).
- City

- Village

- Farming: Produce food.
Farms with Animals:


Fields with Crops:

Production of Energy:
- Nuclear (Mines)

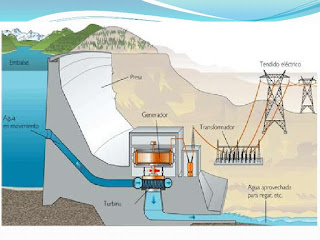
- Hydroelectric (Dams, River Diversion)

- Thermoelectric (Mines)

Negative Impacts on the Environment
- Urbanization:

- Rubbish and Waste.

- Disturbs Animals’ Natural Habitats

- Deforestation

- Industrial Activity: Waste. Consumes energy and pollutes the atmosphere and water, which harms wildlife.


- Transport: Air pollution, noise, energy consumption.


- Farming: Deforestation and pollution (fertilizers).

- Non-renewable energies pollute the environment.

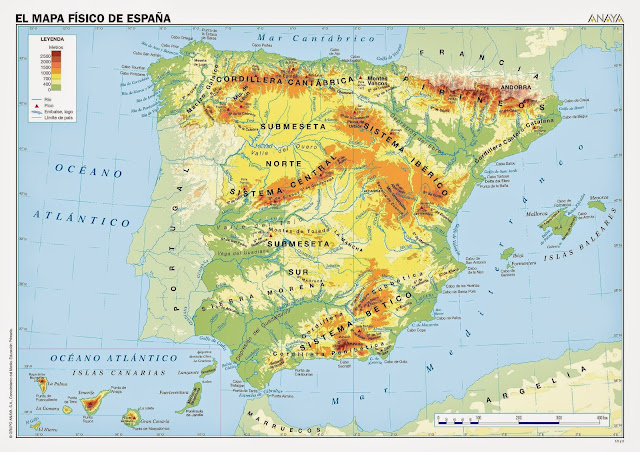
Geography of Spain
Relief

The Central Plateau occupies a large part of the center of the Iberian Peninsula. In it, we find the Central System and the Mountains of Toledo.

The Pyrenees Mountains separate Spain from France.

The Cantabrian Mountain Range is north of the plateau.
The Iberian System is in the east of the plateau.
Sierra Morena is in the south of the plateau.