Probability Problems: Discounts, Training, and Repairs
Sample Question (1) During its grand opening week, Stickler’s bicycle shop offers a “wheel of discount savings.” After customers select the items they wish to purchase, they spin the wheel to determine the discount they will receive. The wheel is divided into 12 equal slices. Six slices are red and award a 10% discount, three slices are white and award a 20% discount, and two slices are blue and award a 40% discount. The remaining slice is gold and awards a 100% discount! 20 10 10 10 100 40 10 10 20 20 10 10 40 Provide all your solutions rounded to 3 decimals (e.g., 0.123).
Part 1: Probability of at Least 40% Discount
Formula: P(At least a 40%) = P(40%) + P(100%) = 2/12 + 1/12 = 3/12 = 0.250
Explanation: The probability of an event A is obtained by the formula P(A) = (Total number of favorable outcomes of A) / (Total Possible outcomes). In the given scenario, the total possible outcomes is 12. The favorable outcomes for 40% is 2 and the favorable outcomes for 100% is 1.
Part 2: Probability of Not at Least 40% Discount
Formula: P(Does not get at least a 40%) = 1 – P(At least a 40%) = 1 – 0.250 = 0.750
The event does not get at least a 40% discount is the complementary event for the event to get at least a 40% discount. The formula for the complement of event A is P(Ac) = 1 – P(A).
Part 3: Probability of 10% or 20% Discount
Formula: P(10% or 20%) = P(10%) + P(20%) = 6/12 + 3/12 = 9/12 = 0.75
Explanation: The probability of A or B is obtained P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) when A and B are independent. In the given scenario, each of the event is independent of the other.
Part 4: Probability of 10% or 20% Discount
Formula: P(10% or 20%) = P(10%) + P(20%) = 6/12 + 3/12 = 9/12 = 0.750
Explanation: The probability of A or B is obtained P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) when A and B are independent. In the given scenario, each of the event is independent of the other.
Part 5: Probability of Two 20% Discounts in a Row
Formula: P(Two customers in a row get a 20% discount) = P(20%) * P(20%) = 3/12 * 3/12 = 0.0625 = 0.063
(2)
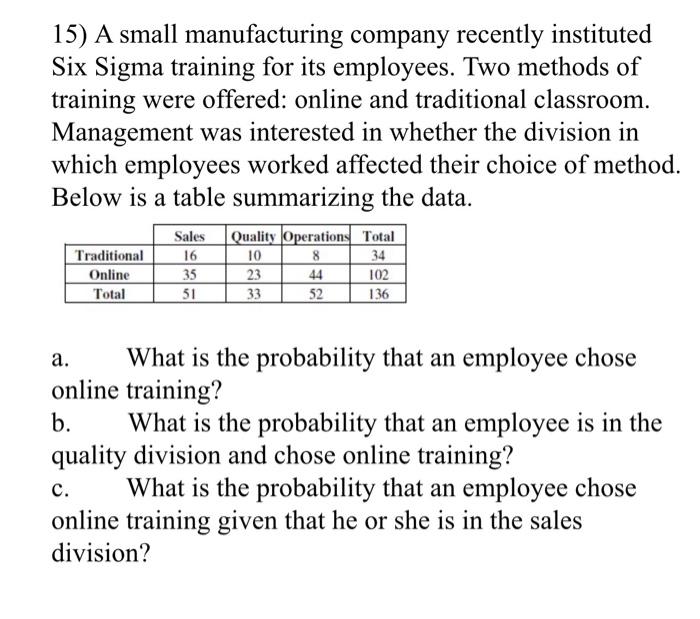
Employee Training Probabilities
a. P(Employee chose online training) = 102/136 = 0.75
b. P(Employee is in quality division and chose online training) = 23/136 = 0.16912
c. P(Employee chose online training | he or she is in sales) = 0.68627
Calculation: P(A|B) = P(A∩B) / [P(A) + P(B)] = 35 / (35 + 16) = 0.68627
Freezer Repair Problem
(3) A fast food restaurant just leased a new freezer and food fryer for three years. The service contract for the freezer offers unlimited repairs for a fee of $125 a year plus a $35 service charge for each repair needed. The restaurant’s research indicates that during a given year 80% of these freezers need no repairs, 11% needed to be serviced once, 5% twice, 4% three times, and none required more than three repairs.
a. Find the expected number of repairs for this freezer per year.
b. Find the standard deviation of the number of repairs per year.
c. What are the mean and standard deviation of the restaurant’s annual expense with the service contract for the freezer?
